According to the present standard of production, the level of technical requirements of fire rescue cushion domestic fire and rescue cushions for collecting domestic and international standards for the reference formulation, this standard part is DIN14151-2002 "Lifesaving then jump."
This standard was proposed by the Ministry of Public Security Fire Department. This standard is under the jurisdiction of the Fifth Technical Committee of the National Fire Protection Standardization Committee.
This standard was drafted by the Ministry of Public Security, Shanghai Fire Research Institute.
The main drafters of this standard: Li Baozhong, Li Yuxi, Han Xiang, Shi Wei, Yin Haibo, Zhu?.
1 Scope  Â
This standard specifies the terms and definitions, models, requirements, test methods, signs, use, storage, routine inspection and inspection rules for fire rescue air cushions.
This standard applies to all firefighting rescue air cushions that are used only when the fire brigade is in emergency and there is no other alternative method. The maximum rescue height is limited to 16m. This standard does not apply to air cushions for training or other purposes.
2 Normative references
The clauses in the following documents have been adopted as references to this standard. For dated references, subsequent amendments (not including errata content) or revisions do not apply to this standard. However, parties that have reached an agreement based on this standard are encouraged to study whether the latest versions of these documents can be used. . For undated references, the latest version is applicable to this standard.
GB/T 1690 vulcanized rubber liquid resistance test method (GB/T 1690-1992, neq ISO 1817:1985)
GB/T 3512 vulcanized rubber or thermoplastic rubber hot air accelerated aging and heat resistance test (GB/T 3512-2001, neq ISO 188:1998)
GB 9969.1 Instruction Manual for Industrial Products General GB/T 10707 Determination of Rubber Combustion Performance Oxygen Index Method (GB/T 10707-1989, neq ISO 4589:1984)
GB/T 19089-2003 Rubber or plastic coated fabrics for the determination of abrasion resistance of the Martindale method GA 124 positive pressure fire air breathing apparatus HG/T 2580 rubber or plastic coated fabric tensile strength and elongation at break Determination of HG/T 3049-1999 Accelerated Weathering Test of Rubber or Plastic Coated Fabrics
3 Terms and Definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this standard.
3.1 Fire rescue air cushion fire rescue air-cushion
It is used only when the firefighting force is used for emergency rescue. It has certain flame-retardant properties and is used to receive air cushions for people who fall freely.
3.2 Ordinary fire rescue air cushion general fire rescue air-cushion
A fan is used to inflate the entire air cushion, so that the entire air cushion is filled with air, so as to achieve a fire-fighting rescue air cushion for undertaking the purpose of free fall.
3.3 Air column type of fire rescue air-cushion
The aluminum alloy liner fiber full-wound composite gas cylinder is used to inflate the air column in the air cushion, and the air column is filled with air to support the entire air cushion, so as to achieve the fire-fighting rescue air cushion for undertaking the purpose of free falling personnel.
3.4 Inflation time
The time from the air supply to inflate the fire rescue air cushion until it reaches a salvageable state.
3.5 Replenishing time the recruiting time
After a rescue, the life-saving air-rescue cushion returns to the rescue state again.
3.6 Safe work area
Fire rescue air cushion surface can ensure the free fall of personnel personal safety area. 
4 models
The fire rescue air cushion product model consists of the class code, feature code, and main parameters. Its type is as follows:
Tag example:
The air-pillar type fire-rescue rescue air cushion with a length of 6m, a width of 5m and a limited rescue height of 16m is model XJD-Z-6×5×16
5 requirements
5.1 Appearance After the fire protection rescue air cushion is fully inflated, the outer surface shall be smooth without obvious creases, and there shall be no abnormal phenomena such as detachment or degumming at the joints.
5.2 Quality The overall mass of the fire-fighting rescue cushion (excluding gas source) should not exceed 100kg when it is not inflated.
5.3 Material of fire rescue air cushion parts 5.3.1 Fabrics 5.3.1.1 Tensile strength The warp and weft tensile strength of all fabrics on the surfaces of fire rescue air cushions shall not be less than 20 kN/m.
5.3.1.2 Aging resistance After all the fabrics on the surface of the fire rescue air cushion have undergone the hot air aging test, the tensile strength reduction should not exceed 35%.
5.3.2 Rubber parts After the rubber parts in the fire rescue air cushion are subjected to the hot air aging test, the reduction value of the tear strength shall not exceed 35%.
5.3.3 Air source The fan used in the fire rescue air cushion shall meet the requirements of the related standards of the air blower, and the gas cylinder shall comply with the provisions of GA124.
5.4 Fire rescue air cushion bearing surface 5.4.1 Marking The central point of the surface of the fire rescue air cushion bearing surface shall be clearly marked with contrasting colors, and the safety work area shall be marked with reflective marks.
5.4.2 Flame Retardant Performance The oxygen index of the fabric of the fire rescue air cushion bearing surface shall not be less than 26.
5.5 The bottom of the fire rescue air cushion touches the ground 5.5.1 Wear resistance After the abrasion resistance test of the floor fabric of the fire rescue air cushion at the bottom, the damage degree shall not exceed the level 2 specified in GB/T19089-2003.
5.5.2 Oil resistance After the oil-resistance performance test of the ground-contact fabric on the bottom of the fire rescue air cushion, the increase in quality should be no more than 15% under the effect of 1# standard oil and -4% to 15% under the effect of 97# unleaded gasoline. Between, and after drying, the surface must not leave any visible traces. 
5.6 Inflation time and replenishment time The time between the start of air inflation from the air source to the fire rescue air cushion and the time when the fire rescue air cushion reaches the rescue state (inflation time) and the recovery time of the fire rescue air cushion in the two rescues (air replenishment time) shall be in accordance with Table 1 regulations.
5.7 Strength Performance Fire rescue air cushions should be free from damage and other anomalies when tested for strength performance.
5.8 Deceleration value The deceleration value of the fire rescue air cushion measured in the deceleration value test shall comply with the requirements in Table 2 (g=9.81m/s2), and the test acquisition time interval should not exceed 3ms.
Table 2
5.9 Stability The fire rescue air cushion shall have no anomalies such as tipping, rollover or damage during the stability test. The load shall not eject the fire rescue air cushion bearing surface or directly hit the ground.
5.10 Reliability The fire rescue air cushion shall be complete, non-damaged or otherwise abnormal after the reliability test.
5.11 Resistance to high and low temperature performance The fire rescue air cushion shall perform an emergency rescue performance test immediately after the high and low temperature performance test shall have no abnormal phenomena such as dumping, side rollover or damage. The load shall not eject the fire rescue air cushion bearing surface or directly hit the ground.
5.12 Gas column type fire rescue air cushion air column airtight After air column type fire rescue air cushion air column is tested for airtightness, its pressure drop should not exceed 0.30 kPa.
6 Test methods
6.1 Visual Inspection Inflate the fire rescue air cushion and visually inspect it after it is fully deployed. The results should comply with the provisions of 5.1, 5.4.1.
6.2 Quality Inspection Weigh uninflated fire rescue air cushions (excluding gas source) with scales or electronic scales, and the results shall comply with the provisions of 5.2.
6.3 Inspection of parts material 6.3.1 Fabric 6.3.1.1 Tensile strength test The warp and weft tensile strength of the fabric shall be measured according to the method specified in HG/T2580 (the width of the sample shall be 50mm), and the results shall comply with the regulations.
6.3.1.2 Aging resistance test The hot air aging test of the fabric shall be carried out according to the method A specified in HG/T3049-1999. The results shall comply with the requirements of 5.3.1.2.
6.3.2 Rubber parts According to the method specified in GB/T3512, the rubber parts shall be subjected to hot air aging tests at 24h and 100°C. The results shall comply with the requirements of 5.3.2.
6.4 Flame Retardant Performance Test of Fire Rescuing Air-cushion Bearing Surface The oxygen index of the surface of the fire rescue air-cushion bearing surface shall be determined according to the method specified in GB 10707. The results shall comply with the requirements of 5.4.2.
6.5 Friction-resistance of the fire rescue air cushion at the bottom of the floor 6.5.1 Wear resistance test According to the method 1 specified in GB/T19089-2003, wear resistance test shall be carried out on the floor surface of the fire rescue air cushion at the bottom, and the result shall be in accordance with 5.5.1. Provisions.
6.5.2 Oil resistance test According to the method specified in GB/T1690, the oil resistance performance test of the floor surface fabric of the fire rescue air cushion at the bottom is carried out. The test time is each 2 h, and the result should meet the requirements of 5.5.2.
6.6 Inflation and replenishment time test The firefighting rescue air cushion shall be laid flat according to the preparatory state before use, and the air source, piping and fire rescue air cushion shall be connected, and the air source shall be activated to inflate the fire rescue air cushion into the fire rescue air cushion for rescue. In the state, use the stopwatch to record the inflation time; after jumping, evacuate the load from the fire rescue air cushion and inflate it into the fire rescue air cushion to the rescue state, and use a stopwatch to record the replenishment time. The result should meet the requirements of 5.6.
6.7 Intensity performance test The fire rescue air cushion is placed on the flat ground according to the rescue state, and a sandbag with a mass of 150 kg±0.2 kg (bottom size of the sandbag is 800mm×500mm) is thrown from its limited maximum rescue height, as far as possible. Falling on the central point of the receiving surface of the fire rescue air cushion and conducting three consecutive tests, the results shall comply with the provisions of 5.6 and 5.7.
6.8 Determination of deceleration value The fire rescue air cushion shall be placed on the flat ground according to the rescue state, and the deceleration measuring instrument shall be respectively installed on the head of a human-shaped sandbag with a mass of 75 kg ± 0.2 kg (see Appendix A for the requirements of the human sandbag). At the chest, pelvis and pelvis, the human form sandbags were thrown from the maximum rescue height defined by the fire rescue air cushion, and they were placed as far as possible on the central point of the fire rescue air cushion bearing surface. Three times from the back touch pad and three times from the foot touch pad. The results should comply with the provisions of 5.7, 5.8.
6.9 Stability test The fire rescue air cushion is placed on a flat surface according to the rescue state. The ball bag with a mass of 75 kg ± 0.2 kg is thrown from its limited maximum rescue height, and it falls to the positions shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 respectively. At the point of impact shown, each is performed once and the test results shall comply with the provisions of 5.9. 
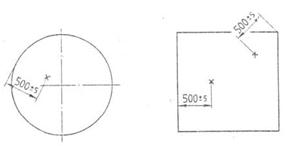
Fig.1 Point of impact of normal type fire rescue air cushion stability test (in mm) Fig.2 Point of impact of air column type fire rescue air cushion stability test 6.10 Reliability test The fire rescue air cushion is placed on the flat ground according to the rescue state. A ball weighing 75 kg ± 0.2 kg shall be thrown from its limited maximum rescue height, and it shall be placed as far as possible on the central point of the receiving surface of the fire rescue cushion, and 50 consecutive tests shall be carried out. The result shall comply with 5.10.
6.11 Resistance to high and low temperature performance test The fire rescue air cushions shall be placed in the ambient temperature of -30°C and +50°C respectively for 24 hours according to their storage conditions. After being taken out, they shall be tested within 10 minutes according to the method specified in 6.7. The results shall meet the requirements of 5.11.
6.12 Air column type fire rescue air cushion air column air tightness test will fill the air column type fire rescue air cushion air column pressure to the rescue state, read the pressure value after parking for 10 minutes, and then park for 30 minutes, the pressure drop value should meet the 5.12 Provisions. Then throw a 75kg±0.2 kg ball sandbag from its limited maximum rescue height and place it as far as possible on the central point of the air-pillar-type fire rescue air cushion bearing surface, and conduct three consecutive tests. The results should be consistent with 5.12. Provisions.
7 Inspection Rules
7.1 Factory inspection Each batch of products shall be inspected by the quality inspection department of the manufacturer, and the inspection items shall be carried out in accordance with 5.1, 5.2, 5.6, 5.7, 5.9 and 5.12 of this standard.
7.2 Type inspection 7.2.1 When one of the following situations occurs, type inspection should be carried out:
a) Stereotype test of new product trial production;
b) After formal production, there will be major changes in structure, materials, and processes that may affect product performance;
c) When the product is normally produced for 2 years;
d) When production is resumed after 1 year of production shutdown;
e) When the national quality supervision agency proposes a type inspection.
7.2.2 The contents of type inspection are all items specified in this standard, and the inspection results shall meet the requirements of this standard.
8 signs
Escape cushions should have the following symbols:
a) Fire rescue air cushion type;
b) Expanded dimensions;
c) Limit the maximum rescue height;
d) total mass;
e) manufacturer's name and trademark;
f) production date;
g) Lifetime.
9 Instruction Manual
The method of preparation of the fire rescue air cushion instruction manual shall comply with the provisions of GB 9969.1. The instructions for use shall indicate: "This product is not intended to be used for training or other purposes," and the words "for use only by the fire brigade for emergency relief and without any alternative means."
10 use
Fire rescue air cushions should be properly used according to their limited rescue height. The life span of a fire-fighting rescue air cushion should not exceed 2 years. If it is found to be abnormal, it should be scrapped in advance.
11 Storage and daily inspection
When the fire rescue air cushion is stored, direct sunlight, rain and moisture shall be avoided, and it shall not be placed together with acid, alkali, oil, corrosive articles and sharp objects. Storage and storage should be kept dry and ventilated. Product storage should be more than 200mm away from the ground and walls. Every three months should be taken out of the inflation inspection once, and with a 50kg sandbag from the test height of 12m according to the test method of 6.7 three times, the results should be consistent with the provisions of 5.6,5.7. It is strictly forbidden for personnel to perform a jump test in daily inspections.
Appendix A Shapes and Additions of Human Sandbags
(Normative Appendix)
Human Sandbag Shapes and Additions A.1 Use human-shaped sandbags without arms, hands, legs and feet as the test load for 6.8. The quality of its nonexistent limbs should be compensated for in the omitted position. The total mass must be 75 kg ± 0.2 kg.
A.2 The replacement of a leg with legs is made of aluminium and has a mass of approximately 5.9 kg. The raised area of ​​the foot is approximately 200 cm2. Its shape is shown in Figure A.1: The unit is mm
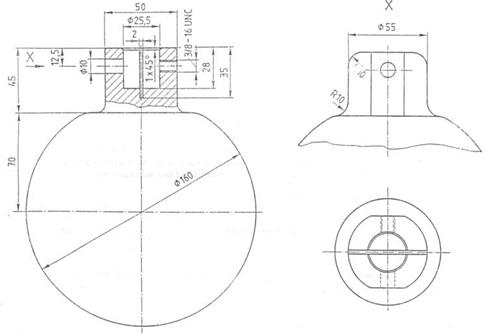
Figure A.1
A.3 The replacement of a small arm with a hand is made of steel and has a mass of approximately 2.15 kg. Its shape is shown in Figure A.2:
The unit is mm 
Figure A.2
Flap Disc
Flap disc, commonly known as flat emery cloth wheels, emery discs, flower impellers or elastic grinding discs, are a large variety of coated abrasive conversion products, which press the cut coated abrasive sheets one by one. It is formed by sticking adhesive to the back cover plate along the circumference. The flap disc are called strong elastic grinding discs. They are made of calcined emery cloth, which uses mesh, nylon, plastic, steel paper and other materials as the base. Attached abrasive tools, evenly distributed in a fan shape to ensure the best grinding effect. The particle size is 36#-320#, 60# and 80# are the most common, and the outer diameter is 4"-7" installed on the angle grinder. Angle grinders are mainly installed on hand-held Power Tools to polish and polish welds, burrs, chamfers, surface rust removal, and surface polishing of various metal and non-metal parts.
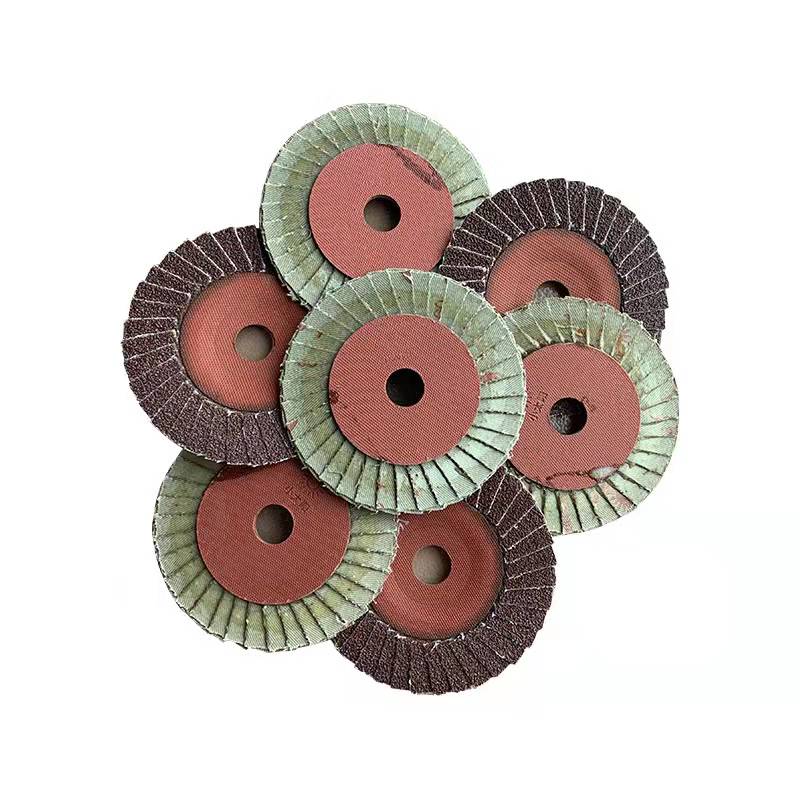

The flat emery cloth wheel (flap wheel) is formed by sticking multiple emery cloth sheets on the tray in a fan-shaped superimposed arrangement, and the bonding angle between each emery cloth and the tray plane is 10°-30°. The emery cloth arrangement of the utility model can make When the abrasive cloth wheel grinds and polishes the workpiece to be processed, the cutting angle is optimized to ensure that the base material of the abrasive cloth wheel and the grinding are consumed simultaneously, which obviously improves the overall wear resistance and grinding efficiency of the flat abrasive cloth wheel, and prolongs the service life of the abrasive cloth wheel. Grind the surface of metallic and non-metallic materials.
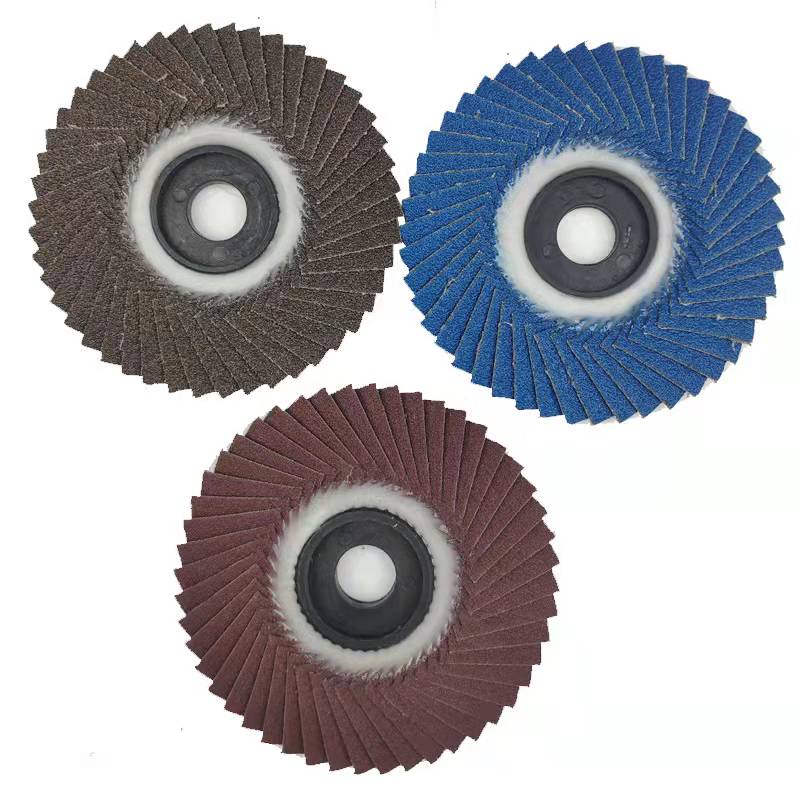

product advantages:
Compared with the resin grinding wheel for fixed abrasives, it has the advantages of polishing and polishing at one time, shortening the operation time, saving the grinding cost, high efficiency, good heat dissipation, high grinding efficiency, reducing operator fatigue, increasing machine life, etc. It has strong elasticity, High tensile and bending strength and good grinding effect. The grinding speed is fast, the effect is good, and the noise during grinding is low. It is suitable for various industries or fields of manufacturing such as major metal parts factories and machinery factories. Good weather resistance, salt spray resistance and heat resistance, suitable for use in different regions.
Scope of application:
It is suitable for polishing of stainless steel, metal, metallurgy, automobile, wood, marble and other industries. It is especially suitable for the processing of stainless steel and can replace the resin-shaped grinding wheel. It has strong elasticity, high tensile and bending strength, good self-sharpening, high grinding rate, and low noise. It is suitable for welding seams in the box. Polishing of the edges.
There are different classifications of louvers according to different angles. The following are two common classifications:
According to the appearance: T27 VS T29
Flap disc generally have two shapes, curved and flat.
The flap disc type is also called the T27 type, and the curved type generally refers to the T29 type.
The flap disc type (T27) has a flat surface. It is mainly used to polish the flat surface and the external edges and corners. The flap disc and the workpiece are angled during work, which can complete the grinding and polishing at one time, reducing the work flow.
The curved surface of the curved louver (T29) has an upward arc, which makes the T29 flap disc have a better cutting ability on the plane. When working, the T29 type grinding wheel forms an angle of 15° to 25° with the grinding surface, which is mainly used to deal with the grinding of contours and edges. When there are higher requirements for speed and cutting ability, T29 flap disc is undoubtedly the best choice.
The related abrasive products we can supply is Flap Disc Adhesive, Bonded Abrasives , and Abrasive Machine such as Flap Disc Making Machine,Abrasive Belt Making Machine, Flap Wheel Machine , Polishing Machine ,Sanding Disc Machine, if you have any needs about abrasive tools, please kindly feel free to contact us.
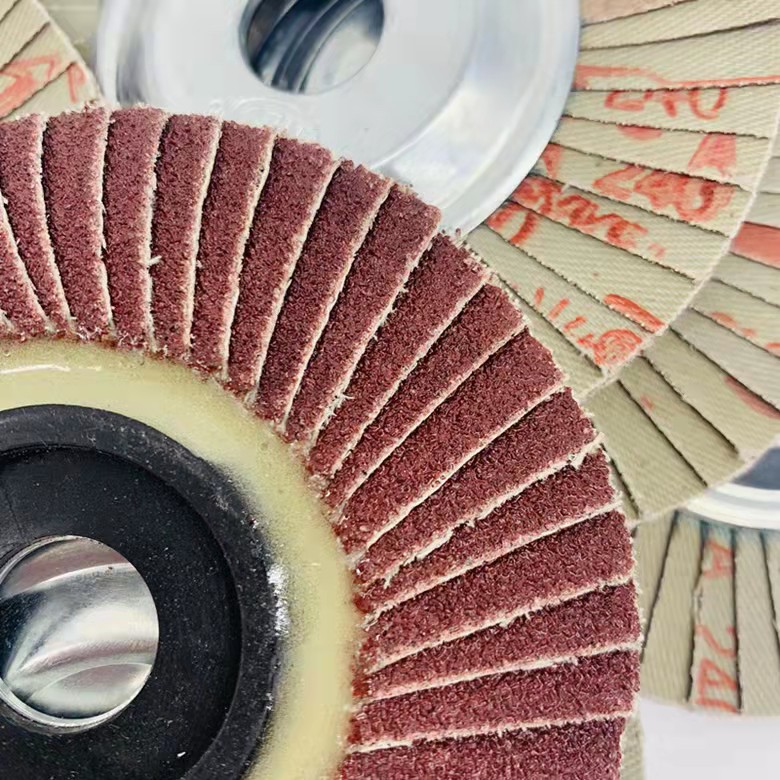

According to the type of abrasive particles: ceramic alumina VS zirconium corundum VS alumina
According to the type of abrasive selected, the flap disc can be divided into three types: ceramic alumina, zirconium corundum and alumina.
Because ceramic alumina itself has many crystals, it has good self-sharpening, relatively neat edges, good heat dissipation, and long service life. Therefore, ceramic alumina louvers are mainly used for the grinding of stainless steel, aluminum and other hard metals.
Zirconium corundum itself is a polycrystalline crystal, with fast cutting speed, good self-sharpening, and strong resistance to high pressure and high temperature. Therefore, zirconium corundum louver blades have strong cutting ability and long service life.
Alumina: single crystal, the cutting ability begins to decline at the beginning of grinding, and the abrasive grains are not easy to break, so the alumina flap disc is suitable for the processing of common metals.
Flap Disc,Flap Disc Machine,flap disk 4.5,Polishing Flap Disc,Sandpaper Flap Wheel
Zhengzhou Jiading Abrasive Manufacturing Co.,Ltd , https://www.jiadingabrasive.com