The use of high-strength steel and ultra-high-strength steel can reduce the structural weight. This grade of steel is becoming more common in portable equipment, lifting gear, and other mechanical equipment.
The lightweight of structural components gives engineers more room to enhance the function of the machine and improve the energy efficiency of the machine.
However, welding thermal cycling can damage certain properties of the substrate. Therefore, welding methods with low heat input must be studied to minimize this effect. In this paper, the experiments of using pulsed MAG welding to reduce welding heat input and improve the mechanical properties of welded parts are summarized. High strength steel and ultra high strength steel are more sensitive to thermal cycling than conventional structural steel. Therefore, this research and development direction is especially meaningful for high-strength steel and ultra-high-strength steel.
For mechanical engineering, the size of the welded joint is one of the most critical factors determining the performance of the finished product. The quality standards and characteristic requirements that the weld site needs to meet are jointly developed by the product designer and the engineer responsible for the weld size. When welding high-strength grade steels, accurate control of heat input is a key factor in meeting the technical requirements of established welded joints. If the heat input is too large, a band softer than the substrate will be formed in the heat-affected zone, which will damage the impact toughness and weld strength. When the heat input is too low, welding defects are more likely to occur. Hydrogen cracking may occur in high-alloy steels and high-strength thick steel plates. This problem can be partially avoided by using preheating and increasing the operating temperature. Improved welding methods and welding equipment can make the work of welders and welding engineers easier.
For the welding of high-strength steel sheets, there is no specific value for heat input.
In contrast, the problem is often caused by excessive heat input: excessive heat input damages the mechanical properties of the welded part. Pulsed MAG welding can achieve lower heat input levels than ball arc welding or jet arc welding.
Pulse welding
In pulsed MAG welding, the wire feeding the wire is controlled by pulse current. Even with the extremely low welding currents common in short arc welding or spherical arc welding, this method can safely transport the filler wire without any risk of short circuit.
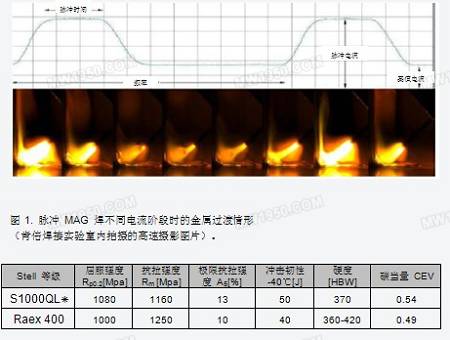
As shown in Figure 1, when the pulse current occurs, the filler droplets will detach from the wire. Figure 1 also shows the following main parameters of pulsed MAG welding:
- pulse current - base current - frequency - pulse time

handheld,infrared,monocular,helmets
Rxiry (Jiangsu) Optoelectronic Co., Ltd , https://www.rxiryrangefinder.com