Enzymatic fuel cells (EFCs) are a type of fuel cells that use redox enzymes as catalysts. They are green, safe, and highly biocompatible. With people's increasing emphasis on clean, safe and efficient energy, and the increasing popularity of wearable and implantable electronic devices, EFCs have received more and more attention. However, due to factors such as low energy density, small power density, poor stability and low voltage, EFCs still cannot be widely used.
The bioelectrochemical engineering research team led by Zhu Zhiguang, a researcher at Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Liu Aihua, a professor at Qingdao University and Elisabeth Lojou, a professor at Aix Marseille University, summarized the working mechanism and development status of EFCs, and explored to solve the above four limiting factors Feasible strategies and methods. Related articles have recently been published in the international review journal Chemical Reviews.
This review summarizes the methods for obtaining high-energy-density EFCs. It is proposed that the use of multi-enzyme cascade reactions can achieve deep or complete oxidation of the fuel to completely release energy; combing the deficiencies of the current EFCs power density calculation method, the geometry of the integrated electrode A new method of power calculation based on factors such as area, specific surface area, electroactive area, weight and battery volume, and systematically evaluated the enzyme electrode interface and EFCs and (super) by improving enzyme activity, promoting electron transfer, using nanomaterials, and designing more effective ) The potential of methods such as capacitor coupling to improve the power density of EFCs; the effects of methods such as enzyme immobilization, enzyme characteristics, protective substrates, and enzymes displayed on the surface of microorganisms to improve the stability of EFCs; Use boost converters to increase the voltage of EFCs. Finally, the article summarizes the latest application of EFCs and makes a prospect for its future development direction.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21706273 and 21878324) and the National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFA0901300). Wu Ranran, an assistant researcher at Tianjin Institute of Workers and Students, is the co-first author of the paper, and Zhu Zhiguang is the co-corresponding author.
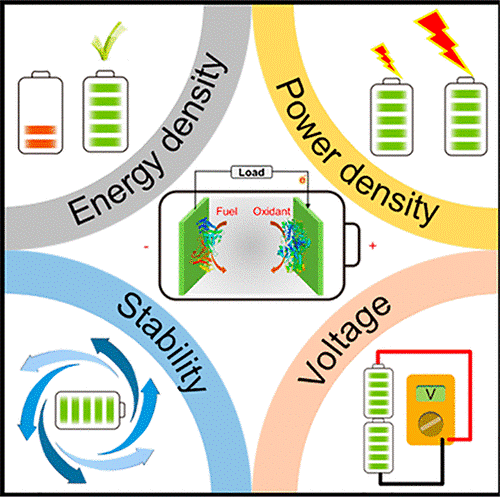
Schematic diagram of enzyme fuel cell and its main problems
Features and advantages of our Railed Tunnel Trolley, tunnel Formwork System. Scientific design makes the roof and side wall surface smooth after second time lining, Optimized mechanic design makes reduce the steel cost of the formwork and save the construction cost, Standard production: full usage of standard parts, develop university of the formwork, makes the Tunnel Formwork to be reused more times.Modernized factory and Certificate of patent.
Tunnel Formwork Trolley,Quickly Assembled Formwork Trolley,Integrated Pipe Gallery Trolley,Pipe Gallery Formwork Trolley
Anshan Lijian Engineering Group Co. LTD , https://www.lijianformwork.com