Energy problems that have plagued Japan for many years may be fundamentally resolved. Systems that generate electricity in space and deliver electricity directly to the ground will be a solution to energy problems. Before the system was realized, basic technologies such as wireless power supply were already in fruition.
The "Universal Plan of the Universe" formulated by the Japanese government in January 2015 contains a "future technology" to promote research and development. That is the “universal photovoltaic power generation system†that allows solar panels to float in the space and transmit the generated electricity to the ground.
This research is still faced with many technical problems to be solved, and the current development cost is expected to exceed 1 to 2 trillion yen. It is said to be realized by the fastest 2040. Although the road is difficult, practical application can change the energy industry of the entire world.
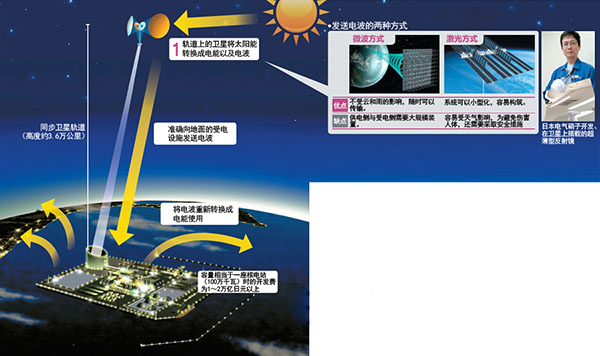
The so-called space photovoltaic power generation is to set up special satellites on the orbit of 36,000 kilometers of high-altitude synchronous satellites, use solar energy to generate electricity in the space, and then convert the electric energy into electric waves and send it to the earth. Finally, the power receiving base on the ground is restored to electrical energy.
In a space where there is no cloud cover, the power generation can be continuously and stably. Therefore, compared with the photovoltaic power generation on the ground, the power generation efficiency is about 10 times that of the latter. Moreover, the method of supplying power to the power receiving base on the ground also has a great advantage. As long as the power-receiving base is built, even where there are inaccessible places such as mountains and seas, it is possible to supply large quantities of clean electricity with zero carbon emissions from the power generation process.
Moreover, the infinite electric energy produced in the space of the universe can also be delivered to other countries from satellites owned by Japan. It is no longer just a dream to transform Japan without resources into an energy exporter.
U.S. freezes development plan and Japan takes the lead
The plan for photovoltaic power generation in the universe was proposed by Dr. Peter Glaser of the United States in 1968. Since then, research and development have been promoted with NASA as the center. But now, for financial reasons, NASA's development plan has been frozen. Although some private enterprises also continue to conduct research, they have not achieved outstanding results.
As a result, Japan, which had been involved in R&D since the 1980s, rushed to the leading position. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the cosmic system development and utilization promotion agency under the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry are jointly developing basic technologies.
"We are leading the world in the country where we continue to carry out research and development," said Yuki Nakamura, director of system development for the development and utilization of space systems.
As shown in the above figure, the space photovoltaic power generation system is roughly divided into three phases.
The first is that satellites set up in space use solar power to convert electrical energy into microwaves or lasers. This is the first stage. The next step is to accurately transmit electric waves to the ground. Finally, the ground antenna is used to receive the electric wave, and it is restored to electric energy again.
One of the biggest issues is satellites. When using the mainstream of past research and development—microwaves as the power supply method, the cost of generating satellites in space is very high.
The use of cosmic solar energy to produce a nuclear power plant, that is, 1 million kilowatts, must lay about 2 kilometers of solar cells in space. If this area is not reached, from the space to the ground, the electric wave will spread during the supply of 36,000 kilometers of electricity. When using the above-mentioned solar cell, a power receiving antenna with a diameter of about 4 kilometers is also needed on the ground.
Due to the huge size of satellites required, the launch costs are naturally huge.
With a power generation volume of 1 million kilowatts, the weight of the material is approximately 15,000 tons. Even if you can launch 50 tons each time, you have to launch 300 times. Therefore, the transportation of materials cannot use disposable rockets, and space shuttles and other reusable space vehicles must be put into practical use. Under this premise, it is estimated that the overall cost will be at least 1-2 trillion yen or more. "Given the profit, it is still difficult to realize with current technology" (JAXA staff).
The power supply is not just the microwave used by mobile phones. JAXA also considers lasers with a wavelength of only about one in 50,000 microwaves.
The microwaves can be powered without being affected by the weather, but as described above, there is a problem that the microwaves cause satellites responsible for supplying power and antennas that receive power to be large. On the other hand, although lasers can realize the miniaturization of the devices, they are easily shielded by clouds and rain and cannot fully exploit the advantages of solar energy in the universe. Moreover, if the antenna is inaccurately charged, it may also harm human health. Both have their own lengths.
In addition to this, there are many issues including how to ensure the installation of a large area for receiving power-receiving antennas and how to obtain the radio wave band used for cosmic photovoltaic power generation.
Taking these circumstances into consideration, the United States decided to freeze the plan. Why does Japan still insist on research?
This can be verified from a verification experiment conducted in Hyogo Prefecture in March 2015.
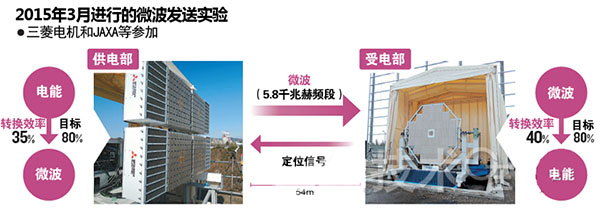
JAXA, propulsion agencies, Mitsubishi Electric, and others conducted experiments to convert electrical energy into microwaves and send them to a powered antenna that is 54m away. The electrical energy obtained exceeded expectations.
The distance between 54m and 36000km seems to be far away, but Nakamura of the advancing agency said: "As long as the signal from the antenna of the electricity-receiving department is established and the technology of accurately transmitting the electric wave can improve the conversion efficiency and extend the transmission distance."
UAV wireless power supply
The microwave power supply and receiving antenna - the two basic technologies that lay the foundation for the photovoltaic power generation of the universe, can also be applied to other fields.
For example, drones can fly for a few tens of minutes at a time. It is still necessary to return to the charging base on the ground before the power is cut off, and if it is powered by microwaves, it can continue to fly.
The use of drones, bridges, and highways, and infrastructure inspections at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant will expand the scope of UAV utilization. There may even be services such as automatic charging of mobile phones in a specific area.
By advancing the magnificent cosmic solar energy plan and accelerating the speed of necessary basic technological innovations to give back to society – for this purpose, the Japanese government decided to continue implementing the plan.
Its effect has also led to other technologies. The development of Japan Electric Glass Glass, which is equipped with glass mirrors for power generation satellites, has expanded the scope of business with the opportunity of cosmic solar energy.
In 2010, JAXA began to reduce the weight of glass by JAXA's requirement to manufacture glass mirrors with a weight of 1m2 and a weight of 100g. In 2014, the world’s thinnest, approximately 0.03mm glass was successfully developed. For the adoption of products such as mobile phones, the company is striving to stabilize production. At the time of review, the executive director of the film business minister Kim Ikumi was saying: "The Cosmos Solar Project has promoted technological innovation."
Although the cost, technology and other topics are numerous. However, it is still too early to abandon the photovoltaic power generation of the universe.
The development and utilization of cosmic systems and the use of propulsion mechanisms have already taken effect in order to realize small-scale power generation systems. Instead of building huge equipment once, they have to launch multiple small satellites. Plans to slowly increase the scale by connecting satellites to reduce costs.
The energy issue is a permanent issue for humanity. As a dream technology that leads humankind to fundamentally solve this problem, the photovoltaic power generation of the universe is highly expected. (Reporter: Yingying Lin, Nikkei Business Weekly)
Common types and uses of pliers
Pliers have many functions and are used in many industries. The pliers used in different industries are also different. Generally, the more commonly used pliers are:
1. Wire stripper
Wire strippers are commonly used tools for internal electricians, motor repairs, and instrumentation electricians. They are composed of knife edges, crimping ports and clamp handles. They are mainly used for stripping plastic and rubber insulated wires and cable core wires.
2. Wire cutters
Also called a vise, it is a kind of clamp and cutting tool. It is composed of jaws, tooth edges, knife edges, guillotines and pliers handles. It is mostly used to pick up nails or break nails and iron wires.
3. Nozzle pliers
It can be divided into electrical and electronic categories. It is mainly used for cutting injection molding machine products, plastic products, and injection nozzles. It is also suitable for cutting metal products and electronic component pins.
4. Needle-nose pliers
Also known as trimmers, pointed pliers, and pointed pliers. They are composed of pointed tips, knife edges and pliers handles. They are generally made of 45# steel. They are used to cut single and multi-strand wires with thinner diameters and to give orders. Stranded wire joint bending, stripping of plastic insulation layer, etc., can be operated in a relatively small working space.
5. Curved nose pliers
Also called elbow pliers, its function is similar to that of needle-nose pliers without cutting edge, and it is suitable for use in narrow or recessed working spaces.
6. Flat nose pliers
It is a commonly used tool for assembly of metal parts and telecommunications engineering. It is generally used to bend metal sheets and metal filaments to make them into the required shape. In repair work, they are used to install and pull out pins, springs, etc.
7. Diagonal pliers
Mainly used to cut metal wires, flat-nose diagonal pliers are suitable for use in recessed working spaces.
8. Top cutting pliers
End-cutting pliers are similar to diagonal pliers. They are mainly used for cutting steel wires with the cutting edge at the top.
9. Water Pump pliers
The function is similar to a pipe wrench, but it is lighter, smaller and easier to use than a pipe wrench. However, the clamping force is not as good as a pipe wrench. Generally, it is only suitable for household non-professional emergency or simple installation of water pipes.
10. Slip joint pliers
The shape resembles a carp. The opening width of the jaws has two adjustment positions, which can be enlarged or reduced. It is mainly used to clamp round parts. It can also replace small nuts and small bolts with a wrench. It is often used in the auto repair industry.
11. Circlip pliers
Commonly known as circlip pliers, it is a special tool used to install inner and outer circlips, and can also be used to remove circlips. .
12. Vigorous pliers
It is mainly used for clamping parts for riveting, welding, grinding, etc. It can also be used as a wrench. Its characteristic is that the jaws can be locked and generate a large clamping force to prevent the clamped parts from loosening.
Wire Stripper,Needle-Nose Pliers,Wire Cutters,Curved Nose Pliers
Rugao Yaou Import & Export Trade Co., Ltd , https://www.ntyaous.com